SINGLE ROW DEEP GROOVE RADIAL BALL BEARINGS are the most widely used bearings and utilize an uninterrupted raceway, which makes these bearings suitable for radial loads, or a combination of radial and thrust loads. This design permits precision tolerances even sat high speed operation.
The cage in this bearing is pressed steel. For high speed bearings, machined brass cages are available. Bearings with locating snap rings are also available.
PRELUBRICATED BEARINGS have integral seal, or shields, which are packed with long-life grease. In many applications, these bearings may be used without supplementary seals, closures, or protective devices. This design offers the lowest possible manufacturing cost to the consumer.
The boundary dimension of this type is the same as the corresponding bearings without the seals or shields.
SHIELDED BALL BEARINGS incorporate securely fastened, steel reinforced, rubber seals, fastened to a groove on the outer ring. Contact with the inner ring is by sealing lip (Contact suffix LLU). Or, non-contact with the inner ring is by labyrinth seal (non-contact suffix LLB) to provide positive sealing at all times.
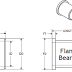
SINGLE ROW ANGULAR CONTACT BALL BEARINGS feature raceways with high and low shoulders. These opposing raceways are designed to carry thrust load in one direction.
These bearings may be preloaded at the factory so that the correct preload will develop within the bearing.
The bearings in this series are assembled with a specific internal clearance so that they will have a specified contact angle under stress load. The standard contact load used by NTN is 30⁰; bearings made to 40⁰contact angle carry the suffix B.
For high speed grinding spindles the 7000C, 7200C and the 7300C series are available. They are high accuracy bearings with a 15⁰ contact angle, and phenolic resin cages for high speed operations.
DOUBLE ROW ANGULAR CONTACT BALL BEARINGS have an inner and outer ring with a double raceway. The two rows are so related that the contact angle is similar to a pair of back-to-back single row bearings. The 5200 and 5300 series offer continuous races, and can carry thrust loads in either direction. Since the 3200 and 3300 series have filling slots, it is necessary to mount them with the thrust load acting against the un-notched face of the rings.
The cage in this bearing is pressed steel. For high speed bearings, machined brass cages are available. Bearings with locating snap rings are also available.
PRELUBRICATED BEARINGS have integral seal, or shields, which are packed with long-life grease. In many applications, these bearings may be used without supplementary seals, closures, or protective devices. This design offers the lowest possible manufacturing cost to the consumer.
The boundary dimension of this type is the same as the corresponding bearings without the seals or shields.
SHIELDED BALL BEARINGS incorporate securely fastened, steel reinforced, rubber seals, fastened to a groove on the outer ring. Contact with the inner ring is by sealing lip (Contact suffix LLU). Or, non-contact with the inner ring is by labyrinth seal (non-contact suffix LLB) to provide positive sealing at all times.
SINGLE ROW ANGULAR CONTACT BALL BEARINGS feature raceways with high and low shoulders. These opposing raceways are designed to carry thrust load in one direction.
These bearings may be preloaded at the factory so that the correct preload will develop within the bearing.
The bearings in this series are assembled with a specific internal clearance so that they will have a specified contact angle under stress load. The standard contact load used by NTN is 30⁰; bearings made to 40⁰contact angle carry the suffix B.
For high speed grinding spindles the 7000C, 7200C and the 7300C series are available. They are high accuracy bearings with a 15⁰ contact angle, and phenolic resin cages for high speed operations.
DOUBLE ROW ANGULAR CONTACT BALL BEARINGS have an inner and outer ring with a double raceway. The two rows are so related that the contact angle is similar to a pair of back-to-back single row bearings. The 5200 and 5300 series offer continuous races, and can carry thrust loads in either direction. Since the 3200 and 3300 series have filling slots, it is necessary to mount them with the thrust load acting against the un-notched face of the rings.